A Test chamber is an essential tool used in laboratories, manufacturing plants, and research and development facilities to simulate a wide range of environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, and pressure, to test and validate products and materials. This controlled environment replicates potential conditions that these items might experience in real-world scenarios. Advanced test chambers can simulate extreme temperature fluctuations, varying humidity levels, and significant changes in altitude.
Also Read Us: Drawing Laminar Air Flow Diagram With Label
Types of Test Chamber:
Test chambers come in different types, each designed for a specific kind of testing. The most common types include:
- Temperature Chambers: Simulate various temperature ranges, from freezing cold to extreme heat, to test how a product behaves under temperature fluctuations.
- Humidity Chambers: Mimic high-humidity conditions, allowing manufacturers to test how their products respond to moisture or water exposure.
- Vibration Chambers: Subject products to vibrational forces, simulating conditions like transportation or use in high-vibration environments.
- Altitude Chambers: Simulate high-altitude conditions, allowing for testing in low-pressure environments.
- Thermal Shock Chambers: Alternate between extreme hot and cold temperatures to test a product’s resilience to rapid changes in temperature.
How Does a Test Chamber Work?
Test chambers work by creating a controlled environment where conditions such as temperature, humidity, or pressure are regulated and maintained to specific values. These chambers typically have various sensors, heating and cooling systems, humidity control systems, and even vacuum pumps, which work together to mimic different environmental factors. Specific technical considerations about the distribution of air within the test compartment make it possible to achieve great uniformity of the temperature values over time and throughout the space of the chamber, ensuring that all parts and surfaces of the DUT are subjected to the same temperature.
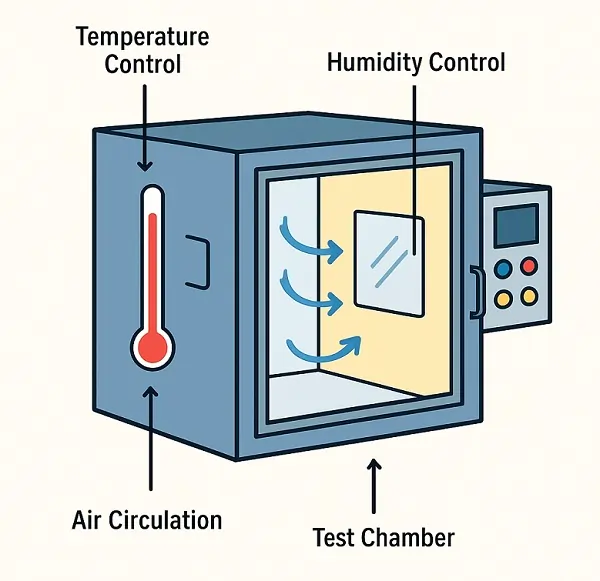
For example, a temperature chamber uses a combination of heating elements and cooling units to regulate the temperature inside the chamber. Similarly, a humidity chamber controls the moisture content in the air by using humidifiers or dehumidifiers. These adjustments are typically controlled via sophisticated software systems, ensuring precise and repeatable testing environments.
When a product is placed inside a test chamber, it undergoes testing cycles that simulate actual conditions the product might face during its lifecycle. This allows manufacturers to assess how well the product performs under stress, whether it’s exposure to temperature extremes, moisture, or physical vibrations.
Why Are Test Chambers Important?
Test chambers are indispensable for several reasons:
- Quality Assurance: Testing products in controlled environments helps ensure that they perform as expected in real-world conditions. This is especially important for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where failure can have severe consequences.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require products to meet specific standards and regulations. Test chambers provide a reliable way to verify that products meet these industry standards.
- Innovation and Development: For businesses looking to develop new products, test chambers allow for rapid testing and improvement of prototypes, leading to faster development cycles.
- Cost Savings: By catching design flaws or weaknesses early in the development process, test chambers help avoid costly recalls and repairs later down the line.
Test Chamber Manufacturer in India
Roch Mechatronics Inc. is one of the leading Test Chamber manufacturers, suppliers and exporters in India. We specialize in design and manufacturing of best quality Test Chambers. The design of test chambers depends on the complexity of the tests they are intended to conduct, ranging from straightforward to highly intricate. They are available in a range of sizes to meet specific testing requirements and manufacturer preferences, from compact bench-top models for small components to large chambers capable of accommodating vehicles. These chambers are used to test products ranging from electronics to aerospace components, automotive parts, and even medical devices. Roch Mechatronics offers Test Chamber at very cost effective prices.
If you’re looking for reliable test chambers to take your product testing to the next level, Roch Mechatronics Inc. the trusted and one of the leading manufacturers and suppliers of test chambers is the perfect choice for you. Feel free to contact us and know more about our products.




